The Generosity of the Maple Tree
A story
In the vast and rugged wilderness of Canada, the people of the First Nations revered the great maple tree, known for its majestic height, vibrant colors, and sweet sap. They believed that the maple tree was a symbol of resilience and generosity, and that it provided them with everything they needed to survive.
For generations, the people of the First Nations used the maple tree for shelter, fuel, and food, and they looked to it for guidance in times of need. They believed that the tree held the power to connect them with the natural world and that its roots reached deep into the earth, grounding them to the land.
One year, a great forest fire swept across the land, destroying homes, crops, and villages. The people of the First Nations struggled to survive in the harsh conditions, but they never lost hope, for they knew that the maple tree would protect and guide them through the fire.
As the days passed, the people prayed to the maple tree for help, hoping that it would send its strength and resilience to them, helping them to withstand the fire and emerge unscathed.
To their amazement, as they sat in silence, a great rumbling sound filled the air, and the ground beneath their feet began to shake. The people looked up in awe as the maple tree split open, revealing a hidden chamber within its trunk.
Inside the chamber, they found a cool and damp space that protected them from the fire. The people huddled together around the maple tree’s trunk, and they felt the power of the tree flowing through them, giving them strength and courage to face the flames.
When the fire finally subsided, the people emerged from the maple tree’s chamber, renewed and invigorated. They looked up at the tree with gratitude and reverence, knowing that it had protected them in their time of need.
From that day on, the maple tree became an even more powerful symbol of strength and resilience for the people of the First Nations. They looked to it for guidance and inspiration, and they knew that as long as the tree stood tall and strong, they would always be protected and guided through life’s challenges.

Botanical description of the maple tree
Maple trees are deciduous trees that belong to the Aceraceae family. They are native to Asia, Europe, and North America and are widely cultivated for their ornamental value, as well as for their syrup, wood, and other products.
Here are some of the key botanical features of maple trees:
Leaves: Maple trees have simple, lobed leaves with distinct veins. The number of lobes can vary from species to species, but they typically have three to five lobes. The leaves are arranged opposite each other on the stem.
Flowers: Maple trees have small, inconspicuous flowers that bloom in early spring before the leaves appear. The flowers are typically yellow, green, or red in color and are arranged in clusters or corymbs.
Fruit: After the flowers have been pollinated, they develop into fruit called samaras. Samaras are winged seeds that are attached to a central stalk. They are often called “helicopters” because they spin as they fall from the tree.
Bark: The bark of maple trees varies in texture and color depending on the species. It can be smooth or rough and can range in color from gray to brown. As the tree ages, the bark often develops deep furrows and ridges.
Size: Maple trees can grow to be quite large, with some species reaching heights of over 100 feet. However, many cultivated varieties are smaller and more compact.
Overall, maple trees are highly valued for their ornamental beauty and for the products that they produce. They are important symbols of fall foliage in many parts of the world and are widely used in landscaping and horticulture.
Leaves of the maple tree
Maple tree leaves are one of the most distinctive features of this tree. Here are some details about the leaves of the maple tree:
Shape: Maple leaves are typically broad, flat, and have a distinct lobed shape. The number of lobes can vary between species, but most maple leaves have three to five lobes. The edges of the leaves can be smooth or serrated, depending on the species.
Size: Maple leaves can range in size from small, at about 2 inches, to quite large, at up to 12 inches in width. The size of the leaf can vary depending on the species and the age of the tree.
Color: Maple leaves are typically green in color, but the shade of green can vary between species. Some maple leaves have a bluish-green or yellowish-green tint, while others are a darker shade of green.
Veins: The veins of maple leaves are very distinct and prominent. They run from the base of the leaf to the tip of each lobe, with smaller veins branching off of them.
Arrangement: Maple leaves are arranged opposite each other on the stem. This means that two leaves are attached to the stem at the same point, with a small space between them.
In the fall, maple leaves turn vibrant shades of red, orange, and yellow, making them a popular choice for autumn decorations and scenery. Additionally, maple leaves are often used as symbols of Canada, appearing on the national flag and in other national symbols.

The flowers of the maple tree
Maple trees have small, inconspicuous flowers that bloom in early spring before the leaves appear. Here are some details about the flowers of the maple tree:
AppearanceA: Maple flowers are typically small and not very showy. They are often yellowish-green in color and can have a somewhat fuzzy texture.
Shape: Maple flowers are usually arranged in clusters or corymbs, which are branched flower clusters with the flowers all at about the same level. The flowers themselves have a very simple shape, with five petals and five sepals.
Pollination: Maple flowers are pollinated by wind, which means that they do not produce nectar or fragrance to attract insects.
Timing: Maple flowers bloom in early spring, often before the leaves appear on the tree. This allows them to take advantage of the available sunlight before they are shaded by the leaves.
Fruit: After the flowers have been pollinated, they develop into fruit called samaras. Samaras are winged seeds that are attached to a central stalk. They are often called “helicopters” because they spin as they fall from the tree.
While the flowers of the maple tree may not be particularly showy, they are an important part of the tree’s life cycle. Without the flowers, the tree would not be able to produce the samaras that allow it to reproduce and spread its seeds.

Fruits of the maple tree
The fruits of the maple tree are called samaras, also known as “maple keys” or “helicopters” due to their winged shape which spins as they fall from the tree.
Some details about the fruits of the maple tree:
Appearance: The samaras are thin, flattened, and shaped like a paddle or a wing. They usually have two wings that are arranged in a V-shape, with a single seed located at the base of each wing.
Color: Samaras are usually green when they first appear on the tree, but they turn brown as they mature.
Size: The size of samaras can vary between species, but they are typically 1-2 inches long.
Dispersal: The wings of the samaras are designed to spin like a helicopter blade as they fall from the tree, allowing them to be carried away by the wind to new locations for germination.
Germination: The seeds of the samaras are coated in a protective layer that allows them to survive harsh environmental conditions until they are ready to germinate. Once they do germinate, the seedling will begin to grow a taproot and develop into a new maple tree.
In addition to being an important part of the maple tree’s reproductive cycle, samaras are also used by children for play and by crafters for various decorative purposes. Furthermore, the winged samaras allow the tree to spread its seeds over a wider area, increasing its chances of survival and reproduction.
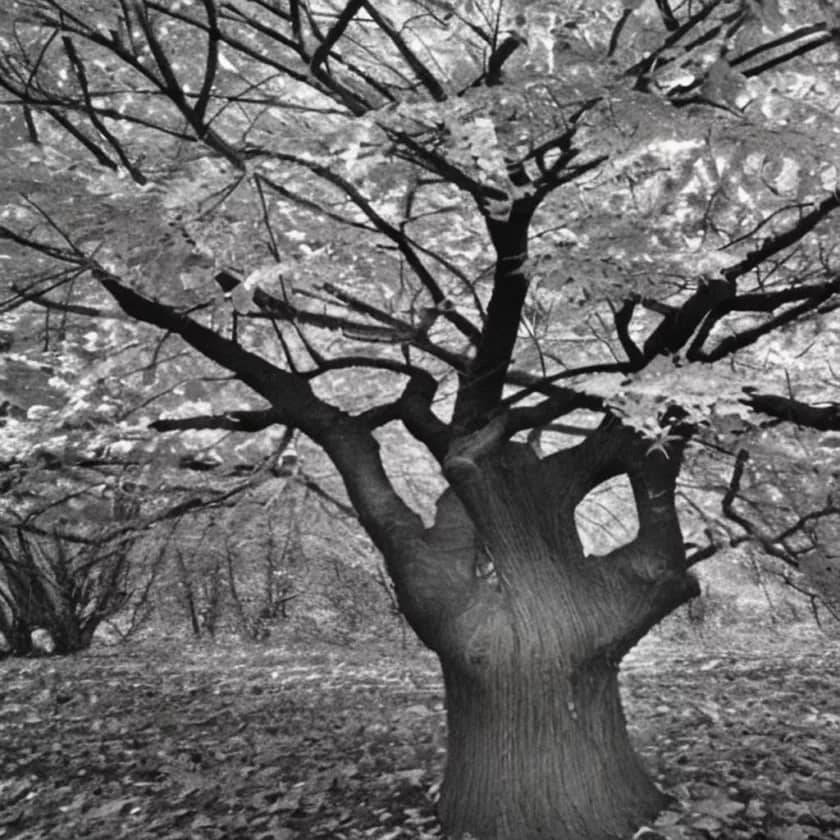

The bark of the maple tree
The bark of the maple tree varies in texture and color depending on the species and the age of the tree. Here are some general details about the bark of the maple tree:
Texture: The texture of maple bark can range from smooth to rough, depending on the species. Young trees tend to have smooth bark, while older trees develop ridges and furrows.
Color: The color of maple bark can vary from gray to brown, and some species have a reddish or coppery tint. The inner bark of the tree is typically lighter in color than the outer bark.
Patterns: The patterns of maple bark can be quite distinctive, with some species having deeply furrowed ridges or peeling layers of bark. The patterns can also vary depending on the age of the tree and its growing conditions.
Thickness: The thickness of maple bark can vary depending on the species and the location on the tree. In general, the bark of the tree serves as protection for the sensitive tissue underneath.
Lenticels: Maple bark has small, raised pores called lenticels that allow the tree to exchange gases with the environment. The appearance and size of the lenticels can vary between species.
The bark of the maple tree can provide important clues for identifying different species of maple trees. Additionally, the bark is an important protective layer for the tree, helping to prevent damage from insects, disease, and environmental stressors. The bark is also a source of tannins, which are used in the production of leather and other products.
Summary of the characteristics of the maple tree
| Characteristic | Description |
| Leaves | Broad, lobed, arranged opposite each other on the stem, distinct veins |
| Flowers | Small, yellowish-green, simple shape, arranged in clusters or corymbs |
| Fruits | Samaras, thin and flattened, with two wings that spin like a helicopter blade when falling from the tree |
| Bark | Texture and color varies depending on the species and age of the tree, with some species having deeply furrowed ridges or peeling layers of bark |
| Size | Can grow to be quite large, with some species reaching heights of over 100 feet |
| Native to | Asia, Europe, and North America |
| Uses | Ornamental value, syrup production, wood, and other products |
The maple tree is known for its distinctive leaves, samaras, and bark. It is valued for its ornamental beauty, as well as for the products it produces. Maple trees are found in many parts of the world and have cultural and ecological significance in various regions.
Maple syrup
Maple syrup is a sweet and delicious syrup that is made from the sap of maple trees. Here are some details about the process of making maple syrup:
Collection: In the late winter or early spring, when the weather begins to warm up, the sap in the maple tree begins to flow. This is the time when the sap is collected for syrup production. A small hole is drilled into the trunk of the tree, and a spout is inserted to allow the sap to flow out into a container.
Boiling: Once the sap has been collected, it is boiled to evaporate the water and concentrate the sugars. This can be done over an open fire, in a specially designed evaporator, or in a modern sugar shack with high-tech equipment.
Filtering: After the sap has been boiled down, it is filtered to remove any impurities or sediment.
Grading: Maple syrup is graded based on its color and flavor. The grades range from light and delicate to dark and robust, with different grades being preferred for different uses.
Bottling: The final step is to bottle the syrup and label it with the appropriate grade and other information.
Maple syrup is a delicious natural sweetener that is used in a variety of dishes, from pancakes and waffles to baked goods and marinades. It is also a significant industry in regions where maple trees are common, such as parts of Canada and the northeastern United States. Additionally, the process of making maple syrup has cultural significance for many communities, who have been tapping maple trees for generations.

Maple Bourbon Sour
A recipe for a tasty drink that features maple syrup as a key ingredient:
Ingredients:
- 2 oz bourbon
- 1 oz freshly squeezed lemon juice
- 1 oz maple syrup
- 1 dash Angostura bitters
- Ice
- Lemon wheel and cherry for garnish
Instructions:
- In a cocktail shaker, combine the bourbon, lemon juice, maple syrup, and bitters.
- Add ice to the shaker and shake vigorously for about 10 seconds.
- Strain the mixture into a glass filled with ice.
- Garnish with a lemon wheel and cherry.
- Enjoy!
This drink is a perfect balance of sweet and sour, with the rich flavor of maple syrup complementing the boldness of bourbon. It’s a great choice for a cozy night in or for sipping on a chilly evening. Cheers!

Ecological importance of the maple tree
There is an important aspect of the maple tree that has not been mentioned yet, and that is its ecological importance. Maple trees provide a range of ecological benefits, such as:
Habitat: Maple trees provide habitat for a variety of wildlife, including birds, squirrels, and insects.
Soil quality: Maple trees have deep root systems that help to improve soil quality and prevent erosion.
Air quality: Maple trees, like all trees, absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, which helps to improve air quality and reduce the effects of climate change.
Water quality: Maple trees help to filter and clean water as it flows through the soil, which helps to improve water quality in nearby streams and rivers.
Biodiversity: Maple trees are an important part of many forest ecosystems and contribute to the overall biodiversity of these systems.
Maple trees are an important part of the natural world and play a crucial role in maintaining the health and balance of many ecosystems. It’s important to recognize and appreciate their ecological value, in addition to their cultural and economic significance.
Shopcorner
Maple tree items on amazon
Thank you for likes, shares and comments! 🌳🌴🌲🌵
Source OpenAI’s chatGPT Language Models, Dalle, AI trot and Fleeky
images Picsart and MIB
Invest in your future
Take time to learn
Embark on your journey in affiliate marketing and website creation alongside an incredible community and myself. Invest in your future by dedicating time to learn and earn. Take all the time you need to master the basics before aiming higher. Give it a try and sign up for free. You won't regret it! Discover the possibilities for yourself...


